Diamond Guide
How to determine a Diamond’s quality and value?
Buying a diamond makes several people wonder about the qualities of diamonds. A diamond’s worth is based on several distinct factors. The diamond industry professionals use a set of particular guidelines which help establish the exact quality and desirability of a diamond. These guidelines, or the 4 C’s, were established by the Gemological Institute of America and are the basis of diamond value estimation. The “Four Cs” – Colour, Clarity, Cut and Carat are few factors that determine the value of a diamond.
Four Cs
A. COLOUR
Diamond Colour is a very vital factor while choosing a diamond. The colour of a diamond has a huge impact on its value. Subtle colour differences can dramatically af-fect diamond value. Best quality diamonds will appear clear and shining whereas low-quality diamonds will exhibit at least hints of yellow or brown. The more yellow the stone, the less value.
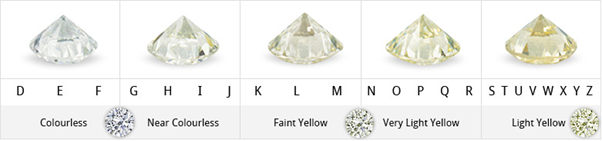
The Gemological Institute of America in the mid-1950 devised a colour grade scale between D - Z to regulate and define the colour spectrum of diamonds. The GIA proposed starting at D as the best and most colourless diamond available. The colour scale progresses through the alphabet from D until Z which is the most colourful diamond.
Nevertheless, one should not confuse coloured diamonds. Coloured diamonds are measured on a different diamond colour scale.
GIA Colour Grading Scale
B. CLARITY
<Diamond clarity is a term used to describe the absence or presence of "inclusions" inside or on the surface of a diamond. Remember, inclusions are naturally occurring. Each diamond is unique, partly because of inclusions. You can view an inclusion as a flaw, or as a naturally occurring and unique characteristic of your diamond.
Diamond clarity is one of the most important factors for selecting and pricing a diamond, in addition to diamond carat and diamond colour.
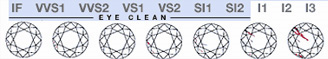
Diamonds having the fewest Inclusions are the clearest diamonds. Diamond clarities are expressed in the following abbreviations
- a. FL or IF (flawless or internally flawless)
- b. I (Visible Inclusions)
- c. SI (Some Inclusions)
- d. VS (Very Slight Inclusions)
- e. VVS (Very, Very Slight Inclusions)
FL or IF are the most expensive ones and I are the poorest.
C. CUT
The cut of a diamond should not be confused with its shape. Shapes are cut from the original rough diamond and whatever the shape, a well-cut diamond will always be able to reflect light better. In nutshell, the cut determines how much it will sparkle!
The brilliance (light return), fire (dispersion of light) and scintillation (sparkle) are hugely dependent on the cut of the diamond. It is the only aspect that is directly influenced by man. When a diamond is cut to the right proportions, light is reflected from one facet to another and then dispersed through the top of the stone.
D. CARAT
A diamond's weight is measured in carats. One carat is equal to 0.2 grams. That means when the carat will be larger than diamond will be heavier.
One Diamond carat is divided into 100 points. Means 0.25 carat diamond is the same as 25 points or 1/4 carat diamond. Carat and cut should be considered together while buying diamond jewellery. This means, if you are choosing a larger carat diamond along with a poor cut grade might appear smaller than a diamond of the same size with the best cut grade.
Talk our expert
If you still want to talk to our expert or member of our customer support team regarding choosing the best diamond colour for you then please call 18008911306 or chat on live chat